
Understanding the Impact and Solutions for a Broken Computer Motherboard
The computer motherboard is the heart of your machine. It serves as the central hub, connecting all components and ensuring they work together seamlessly. But

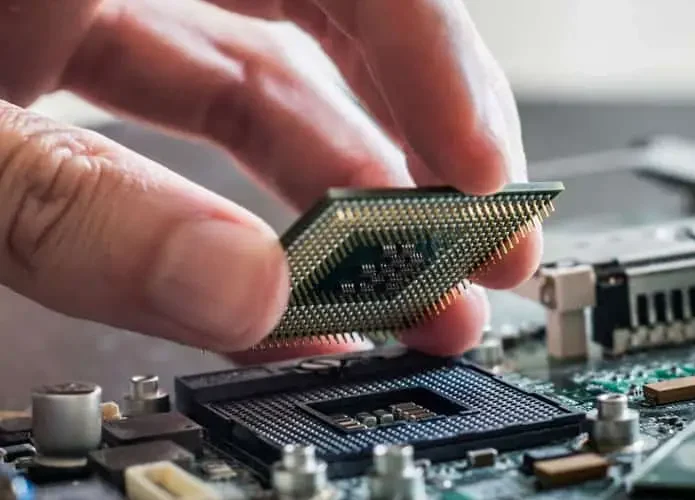
Close-up picture of a CPU (Central Processing Unit) installed in a laptop
Note: The exact method to access system information varies depending on your operating system.Here’s a simple way to identify your CPU on different operating systems:
Win + Pause/Break to open System Properties.lscpu in the terminal.
Motherboard Aorus Asus
Remember, the exact model of your motherboard is key to finding compatible CPUs and other components.Here is a simple list to guide you through the identification process:
It’s vital to match the CPU’s socket type with that of the motherboard to avoid any compatibility issues.Here’s a quick overview of common socket types and their corresponding CPUs:
Remember, even within the same brand, different generations of CPUs may require different sockets.When planning an upgrade or building a new PC, always verify the socket type of both the CPU and motherboard to ensure they match. Mismatched components can lead to installation issues or even damage to the hardware.
Note: Always verify the dimensions of your case to ensure compatibility with the motherboard’s form factor.While the form factor primarily affects physical fit, it can also influence the thermal performance of your system. Smaller form factors may restrict airflow and cooling options, making it essential to plan your build accordingly. Ensuring compatibility between the CPU, motherboard, and case form factor is vital for a successful and efficient build.
Ensure your motherboard’s firmware is up-to-date to avoid compatibility issues.To check compatibility, visit the motherboard manufacturer’s website and look for a CPU support list. This list will detail which CPUs are supported and the minimum firmware version required. If your CPU is not listed or your firmware is outdated, you may need to update the BIOS/UEFI before proceeding.
Make sure your PSU has enough wattage to support all components and some headroom for future upgrades.Here’s a quick checklist to help you evaluate power requirements:
Make sure to also consider the maximum capacity of RAM supported by your motherboard. This ensures you won’t face limitations when planning future upgrades.Here’s a quick reference table for common RAM types and their compatibility:
| RAM Type | Compatibility Note |
|---|---|
| DDR3 | Not compatible with DDR4 slots |
| DDR4 | The current standard for new builds |
| DDR5 | Emerging standard, ensure motherboard support |
It’s important to remember that not all CPUs and motherboards are created equal. Compatibility is key to a successful build.Manufacturers typically organize their compatibility lists by product model, making it easy to find the information you need. Here’s a simple example of what such a list might look like for a hypothetical motherboard:
Remember, while third-party tools are helpful, they should not be the sole basis for your compatibility checks. Always cross-reference the information with the manufacturer’s documentation.Popular third-party checkers include PCPartPicker and BuildMyPC. These platforms not only check for CPU-motherboard compatibility but also for other components like RAM, GPUs, and power supplies, ensuring a comprehensive compatibility assessment.
While immediate compatibility is essential, thinking ahead can significantly reduce future costs and compatibility headaches.Consider the following factors to future-proof your build:
Note: Always check the compatibility of the CPU with the GPU, storage devices, and power supply to avoid performance issues.Graphics cards, in particular, need careful consideration. The CPU and GPU should be matched in terms of performance to avoid bottlenecks. Here’s a simple list to help you evaluate compatibility with other key components:
Ensure your motherboard’s firmware is updated to the latest version to avoid compatibility issues.
If you’re unable to resolve the issue after these steps, consider consulting with the hardware manufacturer or a professional technician for further assistance.In some cases, resolving compatibility issues may require replacing one or more components. While this can be frustrating, it’s important to remember that ensuring compatibility is crucial for system stability and performance. Patience and thoroughness in troubleshooting can save time and resources in the long run.

The computer motherboard is the heart of your machine. It serves as the central hub, connecting all components and ensuring they work together seamlessly. But
When your computer starts acting up, one of the components you may need to troubleshoot is the CPU power supply. In this comprehensive guide, we

Dealing with bent CPU pins can be a frustrating experience for computer enthusiasts and professionals alike. In this article, we will explore various methods to
|
Budget PC upgrade & Repair is now known as Volta PC Upgrade & Repair |